Ovarian Cysts
An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid or other tissue that forms on the ovary. Ovarian cysts will vary in size and number and in most cases are benign (not cancerous).
Ovarian cysts are most commonly found in women who are in their childbearing years. In most cases, ovarian cysts are harmless and go away on their own. Although uncommon, some ovarian cysts may cause problems and will need treatment.
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms will vary depending on the size. Smaller cysts may cause a dull or sharp ache in the abdomen, whereas larger cysts may cause greater pain. Cysts that rupture or bleed may lead to serious problems requiring prompt attention.
TESTING
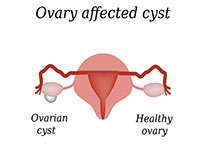 If a patient is suffering from lower abdominal pain, a pelvic exam may be necessary to detect an ovary that is large. The gynecologist may also order a vaginal ultrasound to either identify or rule out the presence of an ovarian cyst.
If a patient is suffering from lower abdominal pain, a pelvic exam may be necessary to detect an ovary that is large. The gynecologist may also order a vaginal ultrasound to either identify or rule out the presence of an ovarian cyst.
In addition to a vaginal ultrasound, the gynecologist may also order blood work if a patient is post menopause to test for ovarian cancer.
TREATMENTS
When ovarian cysts are positively verified, the gynecologist and patient will weigh out the options. As mentioned, many times the cysts go away on their own. If they don’t, birth control pills may be prescribed to treat some variations of ovarian cysts. Birth control pills may reduce the amount of new cysts that form but will not get rid of those already present.
The gynecologist may opt to remove the cysts through a laparoscopic surgery called a cystectomy. Through a cystectomy surgical procedure, only the cyst is removed without removing the ovary. Occasionally one or both of the ovaries may have to be removed depending on the size and type of the cyst, symptoms, age and your desire to have children.
If you or someone you know is suffering from ovarian cyst symptoms make sure to give our office a call for an appointment.