Insulin Resistance
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a characteristic of type 2 diabetes, but not everyone who has insulin resistance (IR) will develop diabetes.
It is usually genetic in origin and tends to run in families. Other factors that can contribute to developing insulin resistance include: inactivity, poor dietary habits, and excess weight gain (which came first – IR or the weight?).
Insulin resistance basically means that the body is making poor quality insulin and has to make more insulin than usual to control the amount of glucose in the blood.
Unlike people with diabetes, the insulin resistant person is able to control the amount of glucose, but it has to work much harder and it is a stress on the hormonal system.
Some Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
- Chronic Fatigue
- High Cholesterol &/or Triglycerides &/or low HDL
- Hypertension
- Inability to lose weight w/low fat diet
- Craving Carbohydrates
- Binge eating after carbohydrate intake
- Sluggishness or fatigue after carbohydrate intake
- GI Digestive Tract Problems
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- Endometrial Hyperplasia (excessive uterine lining due to infrequent menstruation)
- Endometrial Cancer
- Mental confusion
- Frustration from lack of concentration
- Irritability
- Intermittent depression
- Chronic Cystic Acne (into 20s, 30s, & over)
- Thinning hair / early male pattern baldness
- Skin tags
More Information Regarding Insulin Resistance
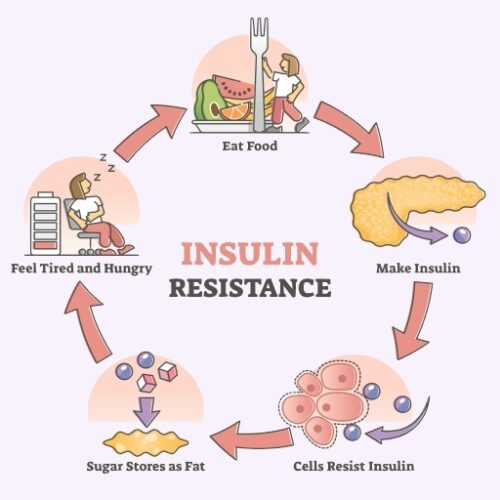 When the insulin’s receptor sites do not fit the receptor sites of the cells, the glucose is not leaving the blood, so the message keeps going to the pancreas that the body needs more insulin. So, the pancreas keeps making and sending more insulin into the blood. In other words, the cells are resistant to insulin, which causes the pancreas to release more insulin in an attempt to regulate blood glucose.
When the insulin’s receptor sites do not fit the receptor sites of the cells, the glucose is not leaving the blood, so the message keeps going to the pancreas that the body needs more insulin. So, the pancreas keeps making and sending more insulin into the blood. In other words, the cells are resistant to insulin, which causes the pancreas to release more insulin in an attempt to regulate blood glucose.
The glucose is then routed to the liver where it is converted to fat for storage. Diet plays an important role in improving insulin resistance and moderating hyperinsulinemia. It is important that glucose is getting into the blood stream at a fairly even rate, as opposed to a little glucose at one meal and a bunch at the next meal. This helps moderate the demands for insulin.
Treatment For Insulin Resistance Includes:
- Medication when indicated exercise
- Aerobic & strength training
- Evenly distributed carbohydrates with protein and reducing caloric intake
-
All of these will help reduce body weight.
Helpful Definitions
Glucose is the main original unit from which carbohydrate-rich foods are made. It is also the basic carbohydrate unit that each cell of the body uses for energy.
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas in response to a high blood glucose concentration. It assists cells in getting the glucose from the blood and into the cell to be used for energy.
Diabetes is classified into 3 categories; Type 1, Type 2, Gestational.
Type 1 is less common than type 2 (~20% of all people with diabetes have IDDM). It occurs when the pancreas quits making insulin. It usually begins in childhood or the young adult years, but people of any age can develop the need to take insulin.
Type 2 accounts for about 80% of all diabetes, and about 80% of these could be prevented with diet & exercise. Type 2 diabetes usually develops slowly and becomes evident after age 40. Being overweight is a common risk factor for this type of diabetes. It can often be controlled through diet and exercise. Medication for type 2 diabetes is usually an oral hypoglycemic agent, but can include insulin injections.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) has been called “borderline” diabetes in the past. It is a degree of hyperglycemia that may precede type 2 diabetes. The glucose and insulin numbers are not normal, but not high enough to be diagnoses as diabetes.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes. Over 40 years of age, close family members with diabetes, have had gestational diabetes, or delivered a baby weighing 9 pounds or more, weight more than 20% over desirable body weight BMI 26 – 29, with other co-morbidities OR BMI > 30, inactive, sedentary lifestyle, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol or triglyceride, history of “blood sugar problems” such as hypoglycemia, insulin resistance, and impaired glucose tolerance.
Gestational Diabetes occurs during pregnancy as a result of changes in hormone levels. It usually disappears when the baby is born, but requires careful control during the pregnancy. Women who have had gestational diabetes or who have delivered a baby weighing 9 pounds or more have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is a symptom of carbohydrate metabolism that is not working a normal fashion. It happens when blood glucose falls below 70 mg/deciliter. When this happens, there is not enough glucose immediately available for cells to produce energy.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia:
- Shaky, dizzy, or weak
- Headache
- Cold sweaty, clam,my feeling
- Confused thinking
- Irritable, cranky, or impatient
- Nervousness
- Hungry
- Rapid heart beat
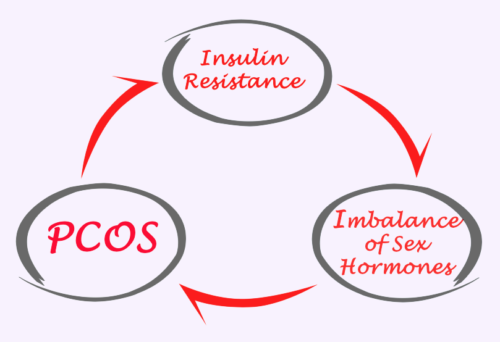
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal imbalance that affects about 10% of women of reproductive age. Symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles and high levels of androgens (male hormones like testosterone).
 Symptoms of PCOS:
Symptoms of PCOS:
- Irregular periods
- Heavy periods
- No periods
- Infertility
- Binge eating
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Increased hunger
- Depression
- Difficulty losing weight
-
Medications That May Be Prescribed For You
These medications are “Diabetic” medications, but if your healthcare provider may prescribe them for insulin resistance or impair glucose tolerance. In this case they are being used for prevention. Actos and Avandia are two brands that accomplish the same thing. They are not used together. Some people tolerate one better than the other.
Some people will need to take Glucophage and either Actos or Avandia.
Glucophage (Metformin is the generic): It keeps the liver from making glucose and increases the sensitivity of cell receptors for insulin.
Actos: Will help the pancreas make better quality insulin by increasing the sensitivity of the insulin receptors.
Avandia: Will help the pancreas make better quality insulin by increasing the sensitivity of the insulin receptors.